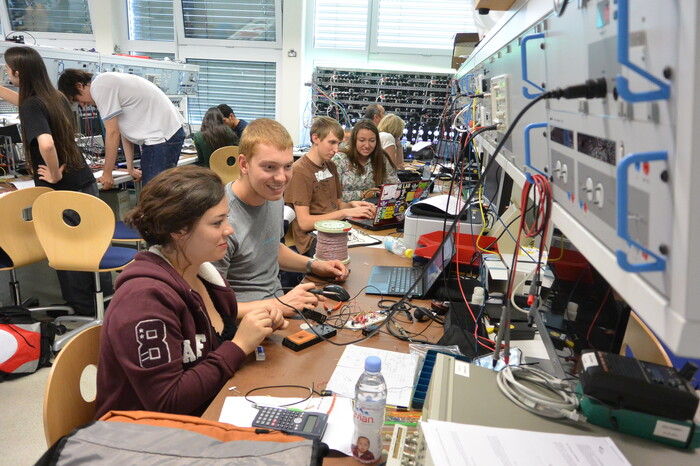
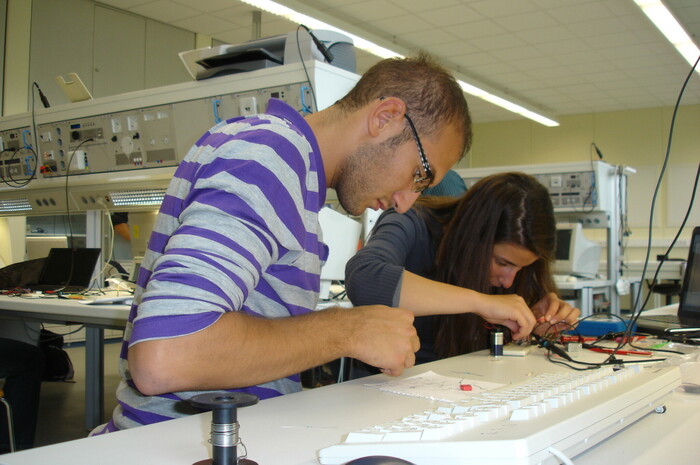
Biomedical Engineering Summer School
Hinweis
Leider findet der Sommerkurs 2025 aus organisatorischen Gründen nicht statt.
Über den Fortschritt der Planung für einen kommenden Kurs 2026 informieren wir hier.
Organisiert von der Jade Hochschule - Fachbereich Ingenieurwissenschaften und International Office
Bitte beachten: Die Unterrichtssprache der Summer School ist Englisch. Sehr gute Englischkenntnisse sind für die Teilnahme daher unerlässlich!
Erfahrungsberichte
Erfahrungsbericht eines mexikanischen Studenten (BME 2022)
Erfahrungsbericht einer mexikanischen Studenten (BME 2022)
Erfahrungsbericht eines marokkanischen Studenten (BME 2022)
Erfahrungsbericht einer türkischen Studentin (BME 2022)
Erfahrungsbericht einer kirgisischen Studentin (BME 2023)
Erfahrungsbericht einer brasilianischen Studentin (Ana, BME 2023)
Erfahrungsbericht einer brasilianischen Studentin (Julia, BME 2023)
Erfahrungsbericht eines brasilianischen Studenten (Mizael, BME 2023)
Erfahrungsbericht eines brasilianischen Studenten (Samuel, BME 2023)
Erfahrungsbericht eines brasilianischen Studenmten (Joao Carlos, BME 2023)
Einführung
Der Fachbereich Ingenieurwissenschaften und das International Office der Jade Hochschule bieten eine dreiwöchige Summer School in Medizintechnik an. Die Summer School umfasst drei Kurslinien mit den Schwerpunkten „Angewandte künstliche Intelligenz", „Grundlagen der Medizintechnik“ und „Biomedizinische Signal- und Bildaufnahme, -verarbeitung und –analyse“.
Unsere alternde menschliche Gesellschaft stellt die Gesundheitssysteme in Bezug auf Kosten-, Qualitäts- und Personalanforderungen vor große Herausforderungen. Der Bedarf an innovativen medizintechnischen Lösungen wächst. Der Einsatz neuester Technologien wird einen wesentlichen Einfluss auf die zukünftige medizinische Versorgung, Diagnose und Linderung von Krankheiten haben. Die technische Innovation kann auch Lösungen wie Telemetrie, fernvirtuelle Beratung und Kontrolle, Prozessautomatisierung und Robotertechnik bieten. Intelligente Implantate, die neue Entwurfsverfahren, Materialien und Software verwenden, können Patientinnen und Patienten so lange wie möglich mobil und fit halten. Früherkennung mit Hilfe präziser Diagnosegeräte, die bildgebende Verfahren, Lab-on-Chip-Analysen und fortschrittliche Sensoren verwenden, kann die Behandlungskosten senken und die Heilungserfolge verbessern. Als eine der Folgen könnte die medizinische Versorgung zu Hause statt in einem Krankenhaus erfolgen, was beispielsweise zu Kosteneinsparungen führen würde.
Ziel des Kurses ist es, eine Einführung in das multidisziplinäre Gebiet der Medizintechnik zu geben, indem die Grundlagen der Entwicklung von medizinischen Geräten im Allgemeinen untersucht werden. Mit einem Fokus auf Anwendungen für Medizintechnologie, Biosensoren und deren elektronische Systeme, Biosignal- und Bildverarbeitung sowie biomechanische Simulation, auch in Kombination mit künstlicher Intelligenz, werden diese komplexen Inhalte in Vorlesungen, Laborarbeiten und Exkursionen erarbeitet. Die multikulturelle Ausrichtung des Kurses wird durch die Präsenz internationaler Lehrender aus mehreren Kompetenzzentren im Bereich der Medizintechnik verstärkt. Ein weiteres wichtiges Lernergebnis dieses Kurses wird durch die Interaktion internationaler Studierender in gruppenbasierten Projekten und organisierten Kulturveranstaltungen gewährleistet.
Die Summer School umfasst die drei oben genannten Kurslinien. Zwei von ihnen richten sich an Bachelorstudierende, während die dritte einen Bachelorabschluss voraussetzt und als Teil des Masterstudiums an der Jade Hochschule und den Partnerhochschulen anerkannt wird. Ein Wechsel zwischen den Kurslinien im Verlauf der Summer School ist nicht möglich.
Die Kurssprache ist Englisch. Die Teilnahme von Studierenden und Lehrenden aus verschiedenen Ländern erfordert die Verwendung einer gemeinsamen Sprache als Grundlage für die alltägliche Kommunikation und Interaktion und stellt eine größere Motivation zur Sprachanwendung dar als es ein Sprachkurs an der Heimathochschule je könnte.
Diese Summer School ist ein Bestandteil des Bachelorstudiengangs Medizintechnik und des Masterstudiengangs Elektrotechnik an der Jade Hochschule und wird von unseren Partnerhochschulen anerkannt.
Kursinhalte
In diesem Sommerkurs bieten wir zwei Kurse für Bachelorstudierende (Lane A und B) und einen Kurs für Masterstudierende (Lane C) an. In den folgenden Tabellen finden Sie eine Beschreibung der jeweiligen Kursinhalte:
Lane A: Applied Artificial Intelligence
Biomedical Applications of Machine LearningGábor Kertész |
| The goal of the lectures is to provide an introduction to image recognition with neural networks, both is theory and in practice. The course starts with a basic introduction to the fundamentals of image recognition using neural networks. On the practical side, Tensorflow and Keras is introduced as the most common frameworks used by machine learning engineers. During the course the students will get an understanding on how Neural Networks are trained, evaluated, and what common problems could occur. After introducing Convolutional Neural Networks, classical architectures are analysed along with modern, state-of-the-art solutions and techniques, which improve the performance of neural networks. Course topics:
|
Biomedical Image ProcessingDániel Kiss |
| This is an introductory course in the fundamentals of biological and medical imaging and image processing, including pre-processing and enhancement techniques, filtering, object detection, and image segmentation. Participants will learn the basics of digital imaging and will gain experience in Python’s image processing abilities. We are also going to meet CellProfiler, an open-source application for batch processing, measuring, and analyzing images. We will see how to use them via real-life examples of various biological experiments covering the following topics. Course topics:
|
Automated Machine Learning and Hyperparameter OptimizationMarcelo Vinícius Cysneiros Aragão |
| This course equips you with practical techniques to streamline your machine learning workflow. You'll gain a strong foundation in machine learning problems like classification, regression, and clustering. The course dives into the world of automation with tools like scikit-learn, auto-sklearn, and Optuna. These tools can automate repetitive tasks in model development, potentially freeing up your time to focus on other aspects. You'll gain practical experience through hands-on exercises building and refining classification, regression, and clustering models using these tools. By the end of the course, you'll be prepared to tackle real-world machine learning challenges. You'll develop the skills to potentially improve model development efficiency using AutoML and HPO. This could translate to time and resource savings. |
Lane B: Fundamentals of Biomedical Engineering
Introduction to Project ManagementDr. Miklós Daróczi, Associate Professor |
| The main objective of the course is to deliver some theoretical and practical knowledge related mainly to the project planning, scheduling and budgeting. The module starts by defining the project and differentiating project management from general management. The project manager’s role, the project life cycle and the elements of project plan are also briefly discussed. The common formats of schedule the Gantt-charts and PERT/CPM networks, some methods of budgeting and cost estimating are also covered. Based on these techniques students will be able to participate in project planning and implementation. Student teams will prepare a report and give a presentation on a special project. The purpose of this assignment is to deepen your knowledge on planning projects and to share that knowledge with the rest of the group. The topic of the project will be selected by the students. |
Basics and Biomedical Applications of MicrofluidicsProf. Dr. Michael Schlüter; Dr. Diana Pinho |
| This Microfluidics course will give a basic overview of micro technologies and the corresponding manufacturing methods (e.g. photolithography, xurography, 3D printing). It furthermore addresses the study of basic and applied aspects of (bio)microfluidics, blood flow in microdevices, and biomedical applications (e.g. PCR-Chip, single cell analysis, plasma separation). This course will introduce participants to microfabrication technologies available for building microfluidic devices, with experimental practice. In the laboratory work, different microfluidic structures for (bio-)medical applications and blood flow studies will be developed, manufactured, and characterized. • Fundamentals of MEMS processing (frontend and backend processes, photolithographic process steps, thin film technology, etching technologies); |
3D Modelling and Simulation of Biomechanical StructuresAlin Totorean, Eng, PhD, Sergiu Galatanu, Eng, PhD |
| The concept of personalized medicine has strongly evolved nowadays and is more and more used in clinical practice. For example, in orthopedics or cardiovascular medicine having patient specific models before interventions proves to be useful for physicians, since it allows them to plan the procedure in advance taking into consideration patient’s details. The process requires 3D models of the anatomical structures and further prototyping or performing computational simulations. This lecture is focused on methods that allow the design of 3D models based on patient-specific medical images (Computed Tomography scans) and to perform a computational analysis using the real model and numerical tools in the area of structural analysis. |
Lane C: Biomedical Signal and Image Acquisition, Processing and Analysis
Amperometric Biosensors and Related ElectronicsDr. Cengiz Koçum, Prof. Dr. Dilek Çökeliler Serdaroğlu | |
| Biosensors are used to detect biological or chemical markers (bio-chemicals, DNA, protein, cells etc.) in order for diagnosis, environmental monitoring and pharmaceutical research. This course represents the fundamental science and engineering concepts of designing biosensors through a common example. Biosensors have three main parts; biorecognition layer, transducers and electronics and they usually produce an electrical signal related to the specific analyte. In this course with lectures and practical exercises students will design and implement the main parts of an amperometric biosensor capable of glucose monitoring. Students will gain an insight of the complexities and design principles of a biosensor from scratch. Course Outline:
| |
| Date | Course Syllabus |
| 1 | Fundamental concepts of biosensors and related electronics |
| 2 | Design, production and pre-tests of biorecognition part of the biosensor |
| 3 | Design, implementation and tests of transducers and electronics part of the biosensor |
| 4 | Integration of biorecognition layer and electronic parts and application of the biosensor |
Instrumentation, Acquisition and Signal Processing for BiosignalsDr. Mehmet Yüksekkaya | |
| Biomedical signals are used to obtain crucial information about human health for diagnosis and treatment follow up. Acquiring biosignals from human body to a computer system is called biosignal acquisition and conditioning. For signal acquisition and conditioning, appropriate electronic instrumentation should be designed. In order to extract the crucial information from the acquired data, it should be processed. This course is designed to be a practical introduction for data acquisition and processing. Students will acquire signals using adequate instrumentation. Further they apply data analysis. After this course, students are able to design a practical data acquisition system. Course Synopsis:
| |
| Date | Course Syllabus |
| 1 | Introduction to biosignal acquisition. |
| 2 | Practical application of microcontroller based system design. |
| 3 | Practical design of a signal acquisition system for biosignal. |
| 4 | Signal analysis and feature extraction. |
Embedded SystemsDr. Gerardo Marx Chávez-Campos | |
| Nowadays, the “Embedded Systems” and its integration with the “Internet of Things” has become crucial for developing healthcare and industrial applications. Thus, to understand the developing process of apps on the embedded system that uses as the central operative system “Linux” are fundamental. Even more, this first approach to the most used operative system on servers, supercomputers, and single devices will guide the student to understand the complete integration of hardware electronics and code for developing from simple to complex tasks. During the course, the student will realize by doing the fundamentals of how to work on the embedded board by accessing hardware, input/output digital ports, read the digital to analog converters. Then, the student will create an application to read and log data into structured frameworks. The registered data will be processed and analyzed using Python. Course Synopsis:
| |
| Date | Course Syllabus |
| 1 | Introduction to the beagle boards and basic applications |
| 2 | Control versions and interfacing electronics |
| 3 | IoT |
| 4 | A final project |
Teilnehmende Hochschulen
Baskent Universität
Fachbereich Medizintechnik
Ankara, Türkei


Universität Ankara
Ankara, Türkei

Instituto Nacional de Telecomunicações - Inatel
Santa Rita do Sapucaí, Brasilien

Morelia Institute of Technology
Morelia, Mexiko

Óbuda-Universität
Budapest, Ungarn


MATE - Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences
Gödöllö, Ungarn

Politechnische Universität Temeswar
Fachbereich Maschinenbau
Timisoara, Rumänien


Westfälische Hochschule, University of Applied Sciences
Gelsenkirchen, Germany
International Iberian Nanotechnology Laboratory, University of Minho (UM), Guimaraes
International Iberian Nanotechnology Laboratory, University of Minho (UM),
Guimaraes, Portugal